What is a Noun? Definition, Types, and Inspiring Examples
Published: 16 Oct 2024
Nouns are like the stars of the language world! They help us talk about everything around us—people, places, things, and even ideas we can’t touch. Whether it’s a common noun like “dog” or a proper noun like “London,” nouns are always ready to make our sentences shine. There are different types of nouns, each with a remarkable job.
Let’s explore these fantastic words together and learn how they bring our thoughts to life!
What is a Noun?

Nouns help us name people, places, animals, objects, and ideas. They appear in almost every sentence and play different roles, like being the subject or object. Nouns can also perform other duties, sometimes acting like adjectives or verbs! They are one of the most important parts of speech that make our sentences come to life.
Example of Noun
- Person: Teacher, doctor, Mary, John
- Place: School, park, Paris, India
- Animal: Dog, cat, elephant, lion
- Object: Car, book, phone, chair
- Idea: Love, happiness, freedom, courage
Types of Nouns:
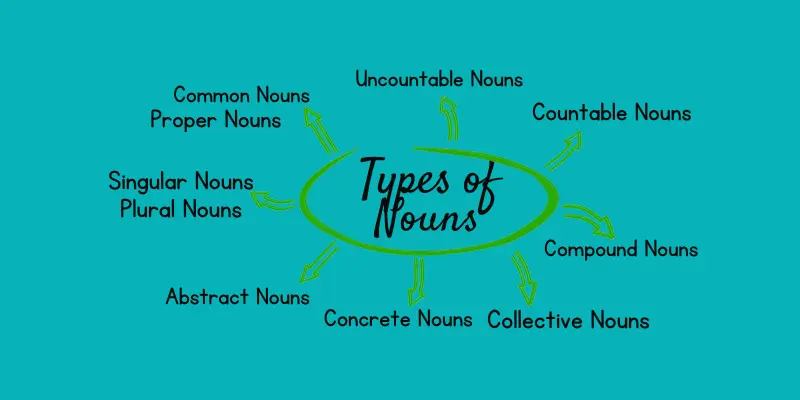
Nouns come in different types, and each type helps us describe what they represent. Each type plays a unique role in sentences and helps us communicate more effectively. Understanding these types of nouns can enhance your writing and make your ideas more straightforward.
- Common Nouns
- Proper Nouns
- Singular Nouns
- Plural Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Collective Nouns
- Compound Nouns
- Countable Nouns
- Uncountable Nouns
Now, let’s discuss each type in detail, one by one!
1. Common Noun
Common nouns are like the everyday words we use to talk about people, places, things, or groups. They don’t name specific ones; instead, they describe general ideas that we see and know.
For example, when we say “dog,” “city,” or “school,” we’re using common nouns. These words help us connect with the world around us.
The cool thing is, we don’t need to capitalize them unless they’re at the beginning of a sentence, so they fit right into our stories and conversations!
Examples
- I have a cat that likes to sleep. (Common animal)
- We went to the zoo on Saturday. (Common place)
- The man is reading a book. (Common person)
- I need a new bag for school. (Common object)
2. Proper Noun
Proper nouns are unique names identifying specific people, places, or things. They always start with a capital letter to show their importance.
Think of proper nouns as the VIPs in the world of nouns! They help us distinguish one unique entity from another, making our sentences clear and precise.
Examples of Proper Nouns:
- My name is Sarah. (particular person)
- This is my cat, Whiskers. (specific pet animal owned by someone)
- Emily traveled to Tokyo. (specific place)
- My favorite book is Harry Potter. (specific book)
3. Singular Nouns
Singular Nouns refer to just one person, place, animal, or thing. They are used when discussing something specific without implying more than one.
For example, “cat” refers to one cat, “city” refers to one city, and “tree” refers to one tree.
Singular nouns help us specify precisely what we mean, making our sentences clear and easy to understand.
Examples
- My teacher gave us a fun assignment. (Single Person)
- The cat is sleeping on the sofa. (Single Animal)
- I read an interesting book last night. (Single Object)
- Paris is a beautiful city to visit. (Single Place)
4. Plural Nouns
Plural nouns refer to multiple people, places, animals, or things. To make most nouns plural, we usually add an ‘s’ or ‘es’ to the end of the word.
For example, “cat” becomes “cats,” and “box” turns into “boxes.” Some nouns change more dramatically, like “baby,” which becomes “babies.” Interestingly, specific nouns stay the same in both their singular and plural forms, like “sheep.”
Some nouns have entirely different spellings when they change to plural, such as “mouse” becoming “mice.”
Examples
- Emma is my best friend. (Specific person)
- Sparky is a playful puppy. (Specific pet)
- My birthday is in April. (Specific month)
- Apple released a new iPhone model. (Specific brand)
5. Abstract Nouns
An abstract noun refers to something that cannot be perceived by our five senses—sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell. These nouns represent ideas, qualities, or conditions we can think about but cannot physically see or touch.
Examples
- Love makes the world better.
- She showed great courage in tough times.
- His kindness towards others is truly inspiring.
- We need to embrace freedom to express our thoughts.
6. Concrete Nouns
A concrete noun is a word for something you can see, touch, smell, hear, or taste. These nouns are all about the things we can experience with our senses.
For example, you can feel a soft blanket, taste a yummy fruit, hear a child laughing, or smell fresh bread. Concrete nouns help us talk about the world in a way we can all understand!
Examples
- The ball rolled across the yard.
- My cat is sleeping on the couch.
- We eat breakfast at the table every morning.
- The tree has lots of green leaves.
7. Collective Nouns
A collective noun is a particular type of noun that represents a group of people, animals, or things as a single unit. It helps us talk about a collection without listing every member.
For example, instead of saying “a group of birds,” we can simply say “a flock.” This makes our language more efficient and expressive!
Examples
- A team of players won the championship.
- A flock of sheep grazed in the meadow.
- A class of students went on a field trip.
- A herd of elephants marched through the savannah.
8. Compound Nouns
A compound noun is a special team of two or more words that come together to create a new meaning.
Sometimes, these words stick together as one word, like “toothbrush.” Other times, they can be two words like “ice cream.”
They can even be joined by a hyphen, like “mother-in-law.” Each form is unique, but they all work together to give us new and exciting ways to describe things!
Examples
Toothbrush (single word)
- I need to buy a new toothbrush.
Ice cream (two separate words)
- We had ice cream for dessert.
Mother-in-law (hyphenated)
- My mother-in-law is visiting us this weekend.
9. Countable Nouns
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted or measured. This means you can have one, two, three, or more of them. They can be singular or plural, and you can use numbers directly with them.
For example, you can say “three apples,” “ten books,” or “four cars.” Countable nouns are easy to recognize because they have both a singular form (like “apple”) and a plural form (like “apples”).
Examples
- I have two cats at home.
- She bought five apples from the market.
- There are three cars parked outside.
- We saw seven birds in the tree.
10. Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns are words that represent things we cannot count individually. They usually talk about things like substances, qualities, or ideas.
This category includes concrete nouns (like water and sand) and abstract nouns (like happiness and information).
Examples
- Water is essential for life.
- I need some sugar for my tea.
- There is a lot of furniture in the room.
- She has great wisdom about life.
The Role of Nouns in Sentences
Nouns as the Subject of a Sentence
When a noun is used as the subject, it usually comes at the start of a sentence. You can find the subject by asking the question, “Who?”
For example, in the sentence “The cat is sleeping,” the noun “cat” is the subject because it tells us who is doing the action.
Examples
- The dog barks loudly.
- Sarah loves to read books.
- The flowers in the garden are beautiful.
- My brother plays soccer every Saturday.
Nouns Used as an Object
When nouns are used as objects, they usually come later in the sentence. You can find them by asking “What?” after the verb. Here are a few examples to help you understand:
- She kicked the ball.
- I read a book.
- He loves chocolate cake.
- They watched a movie last night.
Nouns Used as a Direct Object
A direct object is a noun that tells us what the action is happening to. You can ask “What?” after the verb to find it.
For Example
- She kicked the ball.
- He read a book.
- They watched a movie.
Nouns Used as an Indirect Object
An indirect object is a noun that tells us for whom or to whom something is done. You can figure it out by asking, “For whom?” or “To whom?”
For Example
She gave her friend a gift.
He told his sister a story.
The teacher handed the students their assignments.
Nouns Used as a Complement
When a noun helps to describe or give more information about another noun, it acts as a complement. We can look at two types of complements:
- subject complements
- object complements.
Nouns Used as a Subject Complement
Subject complements are nouns that follow a linking verb and tell us more about the sentence’s subject. They often describe a profession or position.
Examples:
- The sky is blue.
(Here, “blue” is the subject complement that describes the sky.) - My favorite food is pizza.
(In this sentence, “pizza” tells us my favorite food.) - She became a teacher.
(Here, “teacher” is the subject complement that describes what she became.) - The flowers smell wonderful.
(In this case, “wonderful” describes how the flowers smell.)
Nouns Used as an Object Complement
Object complements are nouns that come after the direct object to give more information about it. They can also describe names, professions, or positions.
Examples:
- They elected John the president.
(Here, “president” tells us what John was elected to be.) - The teacher made Sarah the leader of the group.
(In this case, “leader” tells us what role Sarah has in the group.) - The committee appointed Mark as treasurer.
(Here, “treasurer” describes the position Mark was appointed to.)
Multifunctional Nouns
Nouns Used as Verbs
Some nouns can also function as verbs, sometimes with a slight change in spelling. This flexibility adds richness to the English language. Here are a few examples:
- Noun: Run
Verb: Run
Example: I love to run every morning. - Noun: Dance
Verb: Dance
Example: We will dance at the party tonight. - Noun: Drive
Verb: Drive
Example: Can you drive me to school?
Nouns Used as Adjectives
Some nouns can be transformed into adjectives by making small changes to their spelling or by adding a suffix. This allows us to describe other nouns in more detail. Here are a few examples:
- Noun: Beauty
Adjective: Beautiful
Example: She has a beautiful smile. - Noun: Home
Adjective: Homely
Example: They live in a homely cottage. - Noun: Child
Adjective: Childlike
Example: His childlike innocence is charming.
Conclusion
Nouns are indeed the building blocks of our language! They help us talk about everything we see, feel, and imagine, from our friends and family to our favorite places and things. Just think about all the amazing stories we can create using nouns—like tales of brave knights, fluffy kittens, or exciting adventures in faraway lands!
By understanding the different types of nouns—common, proper, abstract, and more—we can express our thoughts clearly and make our sentences shine. Whether writing a story, sharing a joke, or just chatting with friends, nouns help us bring our ideas to life.
So, remember the magic of nouns the next time you write or speak! They’re not just words but the stars of our conversations, helping us connect with others and share our fantastic experiences. Let’s celebrate nouns and use them to create beautiful sentences together!
FAQs
What is a noun and example?
A noun is a word that names a thing (like “computer”), a person (such as “Marie Curie”), an animal (like “dog”), a place (like “Paris”), a quality (like “bravery”), an idea (like “freedom”), or an action (like “swimming”). Nouns can be single words or phrases, such as “apple,” “bicycle,” “shopping mall,” and “breakfast in bed.”
What are the 5 types of Noun?
Nouns are classified into five different types: proper nouns, common nouns, collective nouns, abstract nouns, and material nouns. Each type has its own unique characteristics. For example, proper nouns name specific people or places (like “Eiffel Tower”), common nouns refer to general items (like “city”), collective nouns represent groups (like “team”), abstract nouns express ideas or qualities (like “happiness”), and material nouns denote substances or materials (like “gold”).
How to identify a noun?
Nouns are often described as words that represent people, places, or things, answering the questions “who” or “what” in a sentence. A clear indicator that a word is a noun is when it follows articles like “the” or “a.” For instance, in the sentences “The moon shines brightly” and “I met a musician at the concert,” both “moon” and “musician” are nouns.
What is a common noun example?
Common nouns represent general categories, like “car,” “teacher,” and “park.” They are not capitalized and often used with articles or determiners. In contrast, proper nouns name specific individuals or locations, such as “Toyota” or “Ms. Johnson,” and are always capitalized.
What is verb vs noun?
In grammar, nouns name people, places, or things and often function as the subject or object of a verb. Verbs indicate actions, states, or relationships between nouns. Together, nouns and verbs form essential parts of speech in sentences.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks